
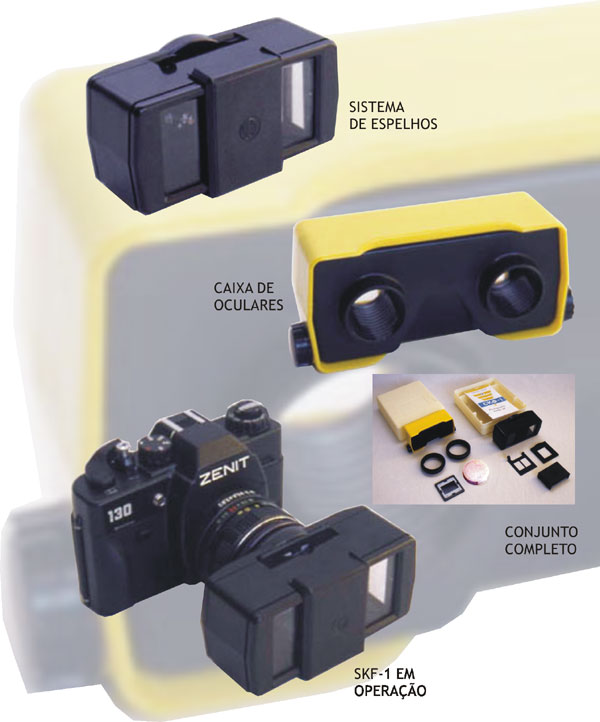
SKF-1
STEREO ATTACHMENT
WORKING
IN CLOSE-UP AND MACROPHOTOGRAPHY
By Luiz Paracampo

I) Foreword
Stereophotogragraphy stands as the top of the art and techniques in the photographic world. The SKF-1 stands in the top of the adapters and splitters models. This article is an overall view of this device emphasizing its properties and versatility.
The first one is its simplicity and ingenuity. Its construction is basically a clever project, As we know, it is the only one to gather in the same device, the adapter for taking photos and slide viewing unit. Its versatility does not ends in this point. Its construction ingenuity lead us to endless adaptations and uses.
You have two adapting tubes for 49mm and 52mm filter threads, although basically developed for the Helios 44 lenses in its various versions, this device will perfectly operate with other lenses with standard 50mm focal lengths (with a small reduction of the homologous* points at infinity).
When using the standard 24x36mm format with the stereoscopic SKF-1 adapter (and all others) the picture becomes vertical, naturally limiting the horizontal taking angle; that way the system is mainly directed to portraits and details of objects.
If you use a 50mm lens you have an equivalent of a 100mm lens, always having a double field in vertical format; in 58mm you will have a 116mm. Take on mind that when using a stereo splitter you have in the camera a true portrait lens system.
To explore the best of that universe, it would be a pity if we could not explore the range of close-up and macrophotography.
The SKF-1 can take great close-ups with Nabla accessory and astonishing macrophotos coupled to Jupiter 9 and UTZ/T extension tubes.
Images obtained with this optical architecture have the same perspective of the normal binocular man seeing and not the parallel sight so common in the high cost devices.
The device only used with the normal lens, limits his operative range in the 2m - 10m range . The close distance is to avoid the hiperstereo effect (giant homologous spacement). The farthest limit is given, because beyond 10m the stereo effect is so dim, that does not catch the observer’s interest.
In order to open new stereoscopic horizons we developed the “Nabla” lens that lets you take stereo photos the normal way on the 0.5 - 1m range.
*homologous = Same point in the image seen in the two pictures of the stereoscopic pair.
We will now show you how.
II) Parts and System
First we show a pictorial schematics for knowing and preparing the device for the various uses.
.
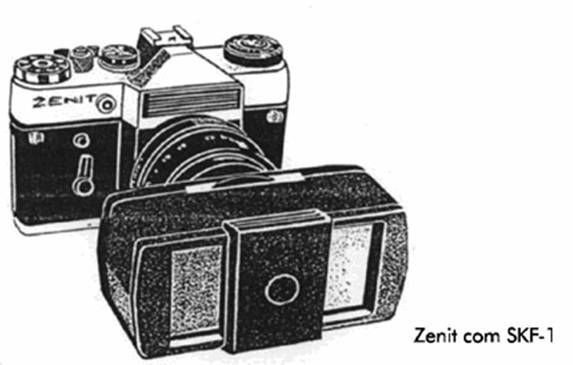
The Zenit camera and SKF-1 splitter
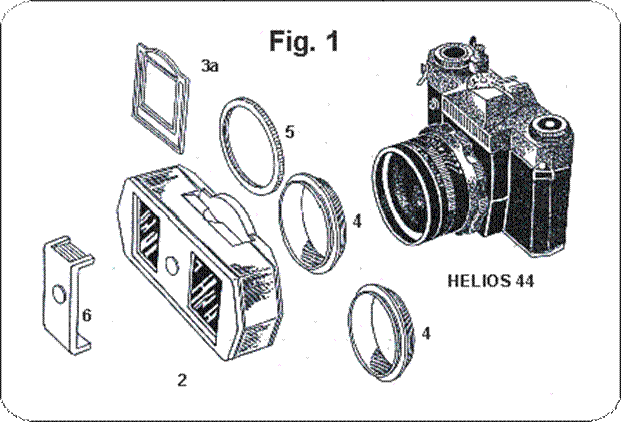
SKF-1 and parts for picture taking
2- Splitter. 3a- Frame. 4- 49 and 52mm adapters. 5- locking ring. 6- sunshade. Helios -44 lens. Zenit camera.
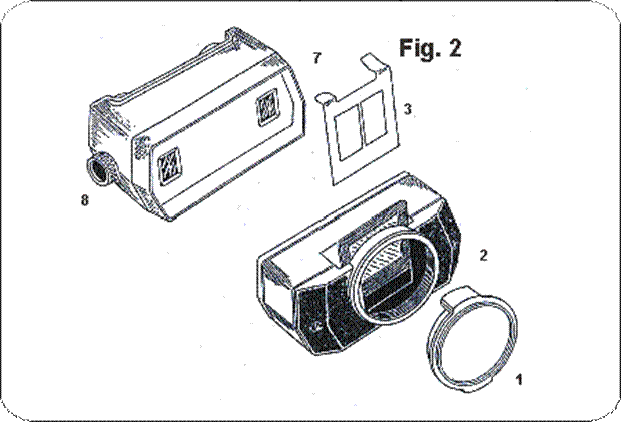
Mounting the device for slide viewing
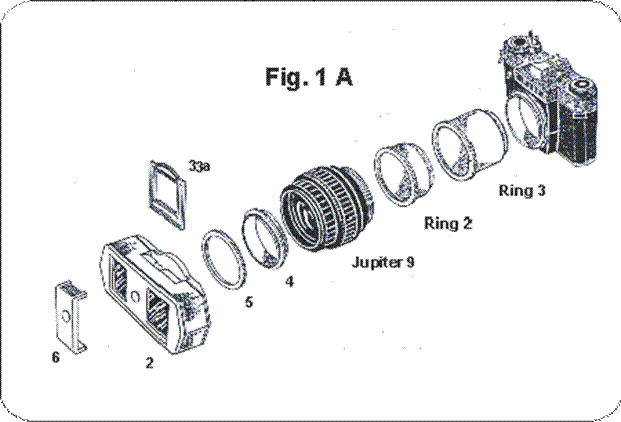
SKF-1 and parts for Macrophotography
2- Splitter. 3a- Frame. 4- 49 mm adapter. 5- locking ring. 6- sunshade. Júpiter-9 lens. Ring 2 and Ring 3 from UTZ/T extension tubes. Zenit camera.
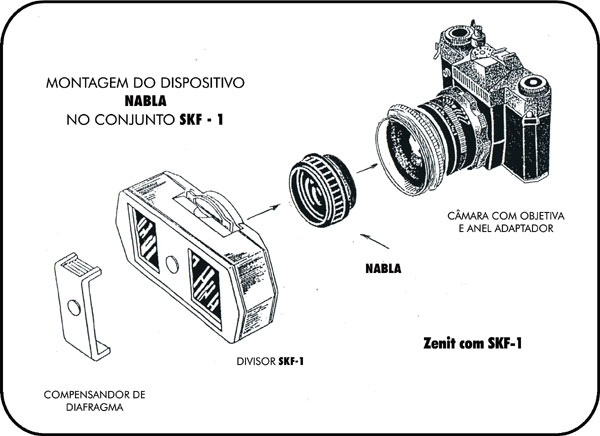
SKF-1 and parts for close-up range
Sunshade. Splitter. 3a- Frame. “Nabla” lens Mounted in the intermal of the 49 or 52mm adapter. Helios 44 lens. Zenit camera.
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
III) Close-up and Macro
A Little bit of teory:
Acording to the distances to be used, high class stereo adapters are made in large or small base. This is because all existing attachments have no automatic convergence, like our eyes which converge when we get closer. Those attachments try to stay in a near parallel viewing in the range they are designed to operate. All similar adapters intended to work with normal camera lens, really DIVERGE when getting closer, and this is due to the optical laws applied in lens movement, during focusing.
-
That is, -All commercial adapters including the costly ones, operate exactly at
the REVERSE way they would do. -
That way, according to the photographers’ needs, there are made at least two
versions of interpupilary devices on these stereoscopic accessories in order to
minimize the project errors of such devices. This complicates the use and
increases the investment in such systems.
When you use unit focusing lens, (as are all Helios 44 lenses), the lens
increases its focal length when getting closer but its mechanical extension
becomes greater yet and the incidence of the new virtual axis create a
divergence of the two images. (the center point of them becomes progressively
greater as we get closer). When you use front cell focusing lenses the formed
objective reduces its focal length when getting at closer distances, the optical
block although maintains the same distance from film plane -- Which is worse
yet.
Solution: Get closer by simultaneous lens focal length increase and reduction of
the needed mechanical extension. This can done by two methods:
1) Using the “Jupiter 9” 85mm lens and extension tubes when in Macro photography, Or …
2) By the additional placement of “Nabla” lens over the “Helios 44” in close distances - as we will show further.
These solutions give a superior viewing perspective of the image when compared with other type of devices. This is due the that they are nearer the natural man’s seeing.
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Working principles
And now we have the -How it works- pictorial side of the - Little bit of teory- based on the explanations above.
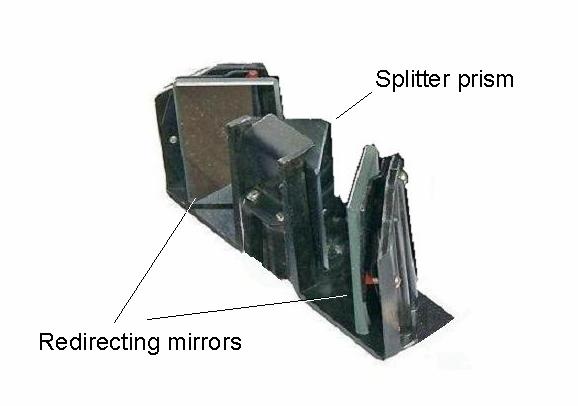
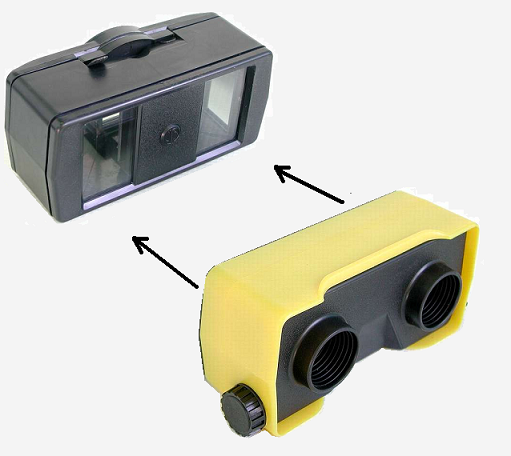
SKF-1 Internals
This device is composed of a mirrored central splitter prism and two redirecting external mirrors.
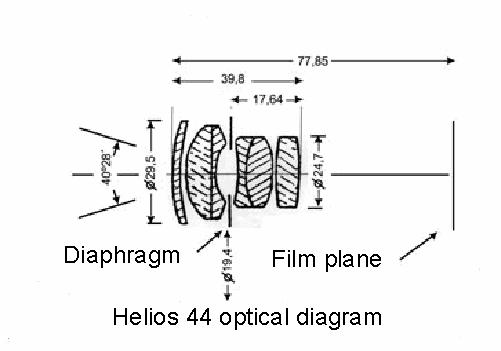
Helios 44 optical diagram and real dimensions
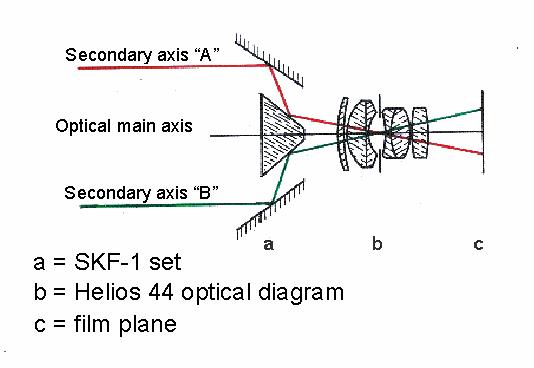
SKF-1 with Helios 44 set at infinity
Trace of rays
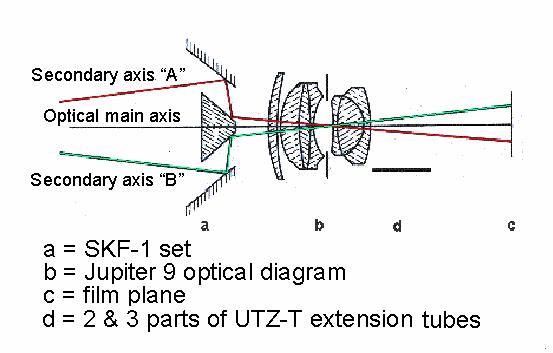
SKF-1 with Jupiter 9 set at macro position
Trace of rays
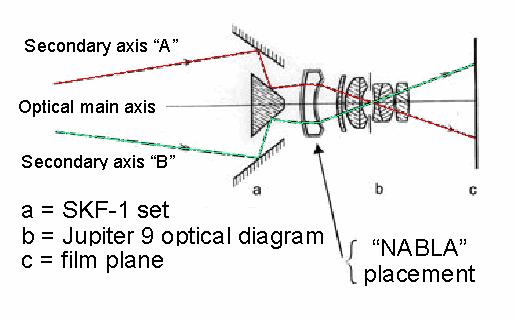
SKF-1 with Helios 44 and NABLA lens set at close distances
Trace of rays
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
IV) SKF-1 used in projection for instant Auto Stereoscopy.
This is an other almost unknown use of the SKF-1 device - Projection. Specifically Autostereoscopy. Easy, the same way you can take a picture, you do the reverse –The projection. Doing this, every possible optical error is automatically corrected. This is the technique used for precision measuring in aerophotogrametry.
Autostereoscopy was successfully experimented in Russia in the years 1930s where the idea was born. We again give a rebirth in this interesting idea. In the links, you can see a detailed description of the system.
Working with Helios 44 and Nabla, in the reverse way (Projection) you have perfect images at a chosen optimum distance from the screen , and you can see stereo with free eyes the same way you see the surrounding objects.
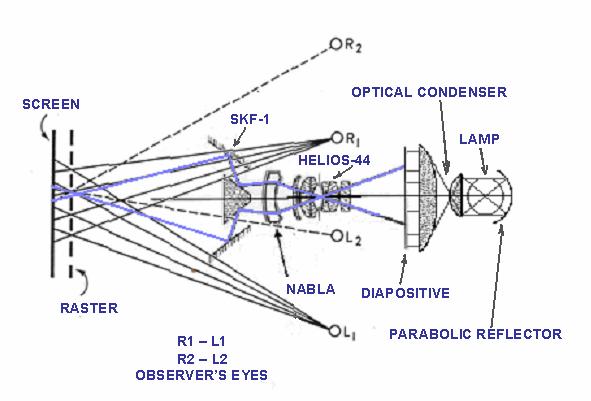
Diagram of SKF-1 used in projection
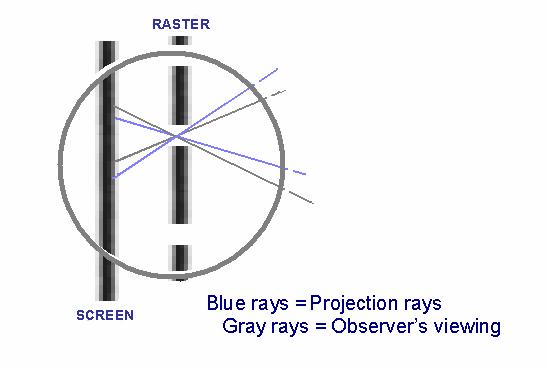
Details of the image formation in the screen behind the raster.
This proposal is an adaptation of old Russian experiment in the field
You can see more explanation about at links, in the end of article.
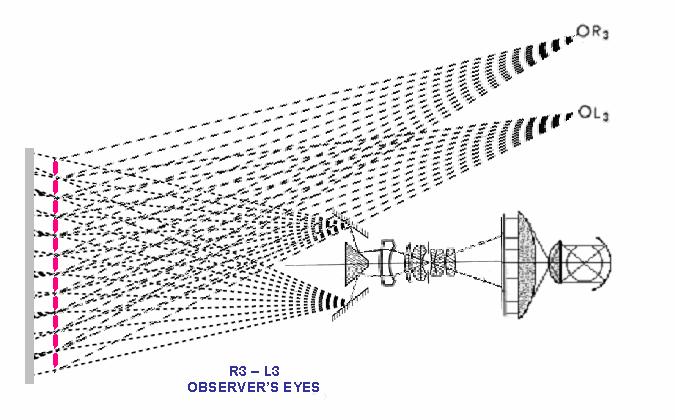
Stereoscopic projection and viewing zones diagram
Interpupilar = 65mm
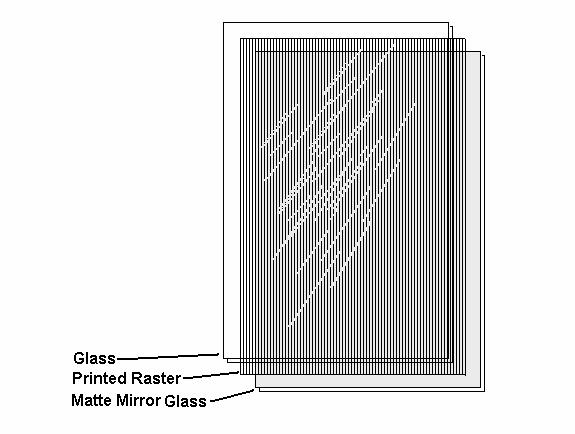
Construction of an Autostereoscopic projection raster
Size A4: One clear glass, one raster film and one mirror over glass sandwich.
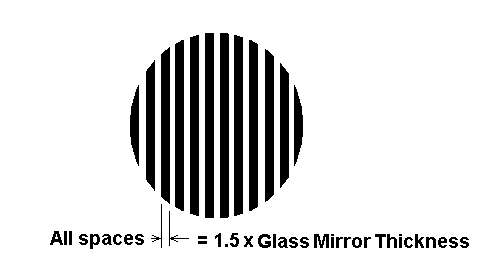
Construction of an Autostereoscopic Raster film
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
V) These are the SKF-1 companions

SKF-1 splitter unit used as diapositive viewer

Helios 44

Jupiter 9

Tubes UTZ/T

Nabla Auxiliary Lens
Know that several cameras can be fitted with the SKF-1 for taking stereo pictures.

With a proper adapter SKF-1 can also be used on a variety of cameras
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Links:
An extended explanation of the various existing stereo adapters could be seen at: ( in Portuguese language)
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo7.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo8.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo9.htm http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo9b.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo1.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo2.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo3.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo3a.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo4.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo5.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo6.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo10.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo11.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo12.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo13.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo14.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo15.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo16.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo17.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo18.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo19.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo20.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo21.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo22.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo23.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo24.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo25.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo26.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo27.htm
http://www.novacon.com.br/sistereo28.htm
xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Appendix:
VI) Nabla
CONVERGENCE DEVICE FOR SHORT DISTANCE STEREOSCOPIC PICTURE TAKING
Normal senses are
higher at close distances. And that is true also for photography. The “Nabla”
enables one to take pictures in the close range of 0.5 to 1m , taking advantages
of the aparent increased focal length of the lens when working
stereoscopically. Just when you want to see details. The Nabla device
reproduces the man’s close distance viewing at its best. It increases lens focal
distance around
(~+2%) .
a) Close-up
Nabla is a close-up lens specially designed to work together the “SKF-1”. This lens is placed in the inner part of any of the “SKF-1” coupling tubes delivered with the set. (49mm or 52mm tubes). Different from a commom close-up used in monoscopic photo, this lens is a negative meniscus having –0,43D. Construction properties of the “SKF-1” enables to this further development.
b) Macro Photography
The “SKF-1” can also be used in the macrophotography, together “JUPITER-9” lens and nº 2 & 3 rings (the larger ones) of the “UTZ-T” set. We will obtain a 1:2,4 image scale reduction. See the ray tracing lines in the “HELIOS-44” and “JUPITER-9” & tubes, the respective diagrams.
